- 1 课程回顾
- 2 概述
- 3 term
- 4 eshell
- 4.1 eshell 的好处
- 4.2 eshell 的基本配置
- 4.3 eshell 的 alias
- 4.4 eshell 里的 C-d
- 4.5 eshell 的命令历史
- 4.6 有些命令使用 term
- 4.7 修改下 eshell 的主题
- 4.8 eshell-syntax-highlighting 语法高亮
- 4.9 capf-autosuggest自动补全
- 4.10 eshell-up快速进入父级文件夹
- 5 结语
1 课程回顾 🔗
通过上节课的学习,我们了解了如何在 Emacs 里看 RSS 文章,通过 elfeed 强大的标签和搜索机制,我们可以愉快地在 Emacs 里阅读信息流。
今天我们学习在 Emacs 里使用 Shell。
2 概述 🔗
Emacs 被称为是一个“操作系统”,不是没有原因的,因为你几乎可以在 Emacs 里做任何事,这里自然就包含了 Shell。Emacs 里有各种使用 Shell 的方式,有些是终端模拟器,有些是完整独立的 Shell:
这里,我推荐的是 eshell ,其他的 shell 我们可以使用 iterm2 这样的软件来达到类似的目的,而 eshell 恰恰是 Emacs 独特的 Shell,它是完全由 Emacs Lisp 实现的独立的 Shell,它不是一个终端模拟器,它有一些独特的特性,尤其和 Emacs 集成的很好。
3 term 🔗
term 是 Emacs 自带的 Shell,我们在 Emacs 里直接运行 M-x term 即可使用,会提示我们选择哪个 shell 程序(如 bash、zsh):
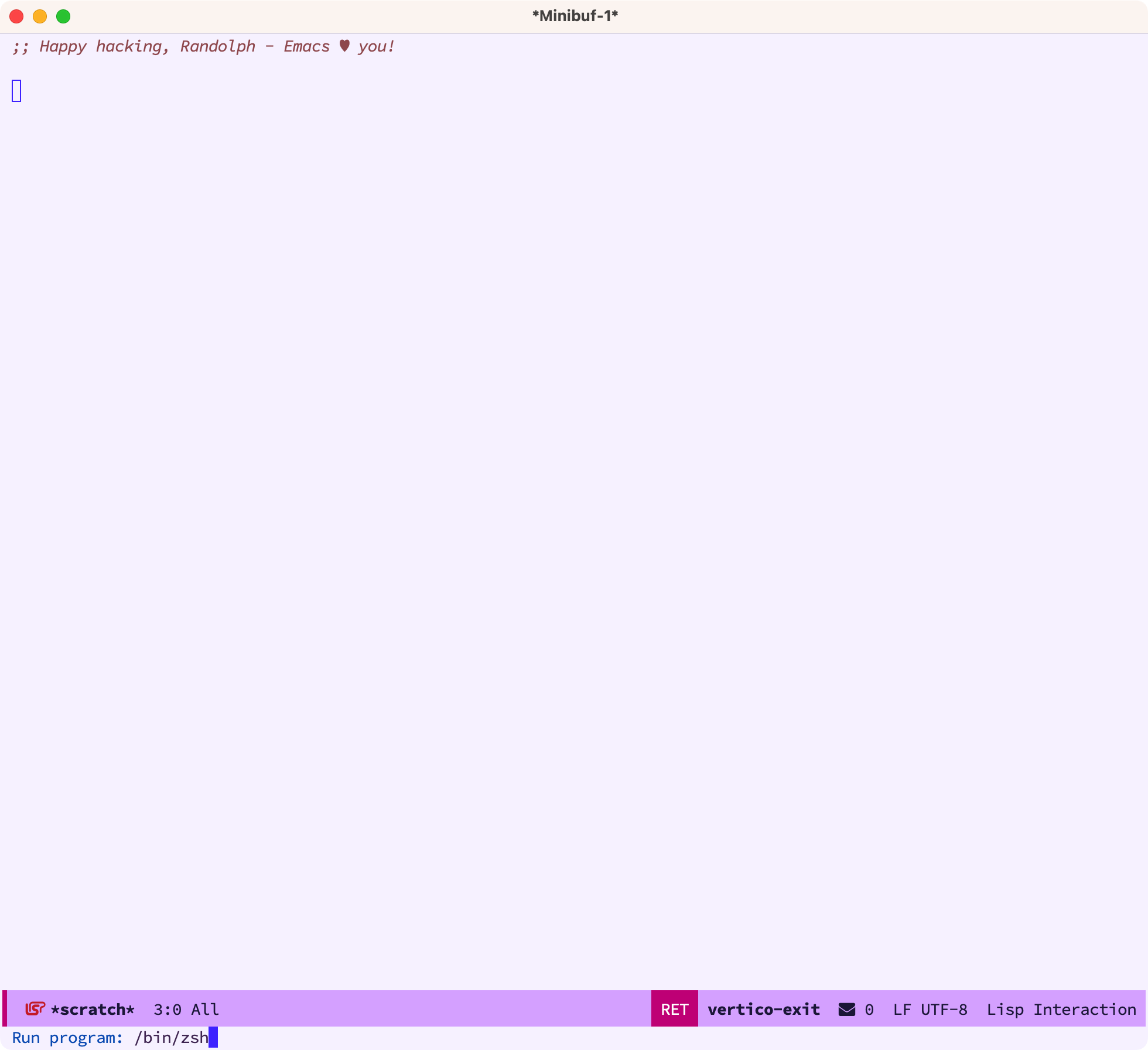
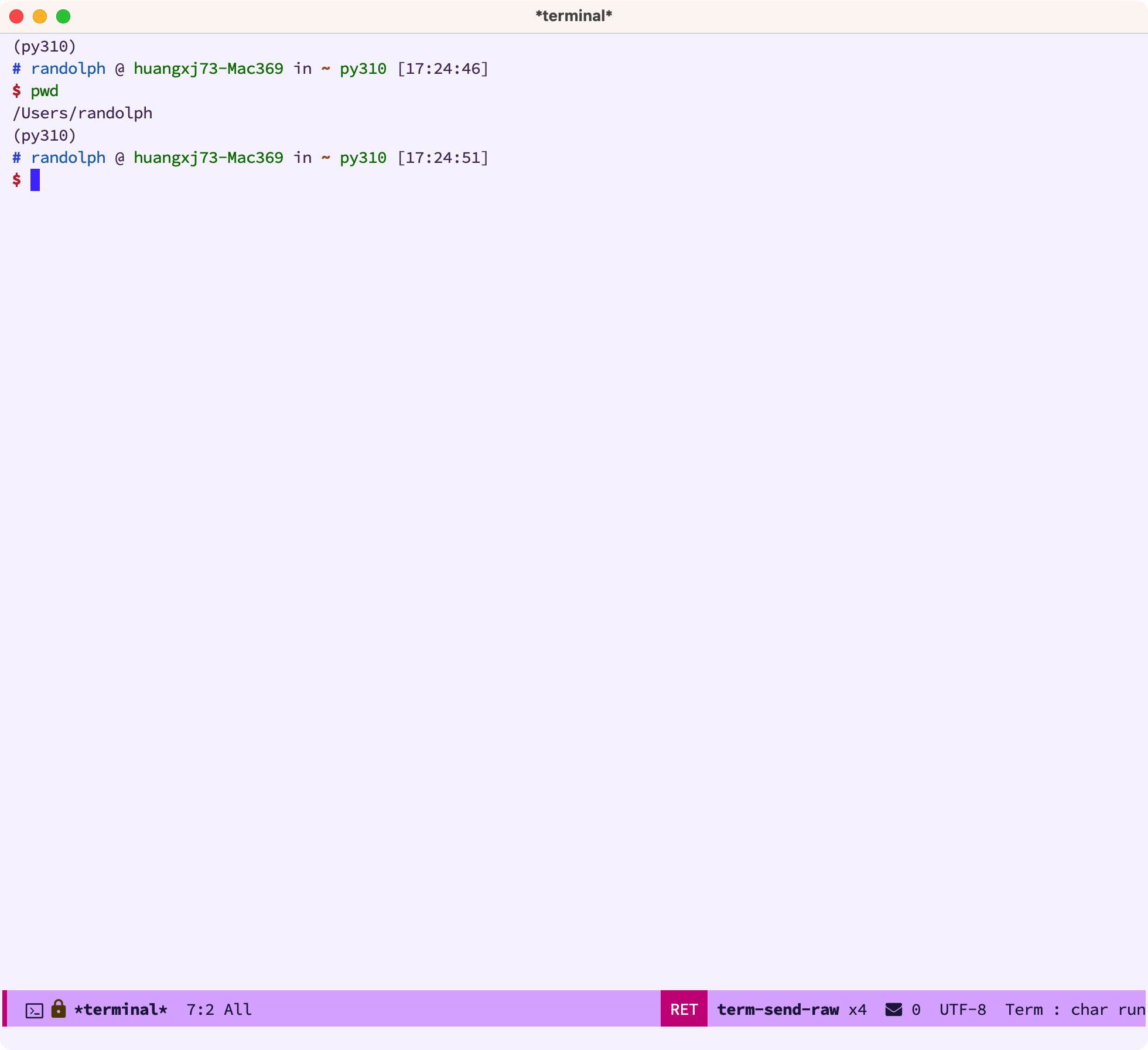
我们选择 zsh 后,就直接会进入到 term ,使用体验跟我们在 iterm2 里几乎是一致的:
4 eshell 🔗
4.1 eshell 的好处 🔗
那么使用 eshell 到底有哪些好处呢?我们参考这篇文章 Mastering Eshell 可以看到,eshell 有如下好处:
- eshell 是一个完整的独立的 shell,如 bash 和 zsh 一样,而不是模拟器
- 原生 Tramp 支持
- 写 Elisp 而不是 sh
- 通过 Emacs 来重定向和管道
- 命令拦截:如
grep命令会使用 Emacs 的 grep 机制而不是类似其他 shell 的机制 - Plan9 智能显示
- 因为完全由 Elisp 实现,所以可以自由扩展
- 在 eshell 里可以直接执行 elisp 函数或表达式
- …
例如,我们可以直接在 eshell 里运行 Elisp 命令,如 find-file xxx ,他会找到 xxx 文件并打开:
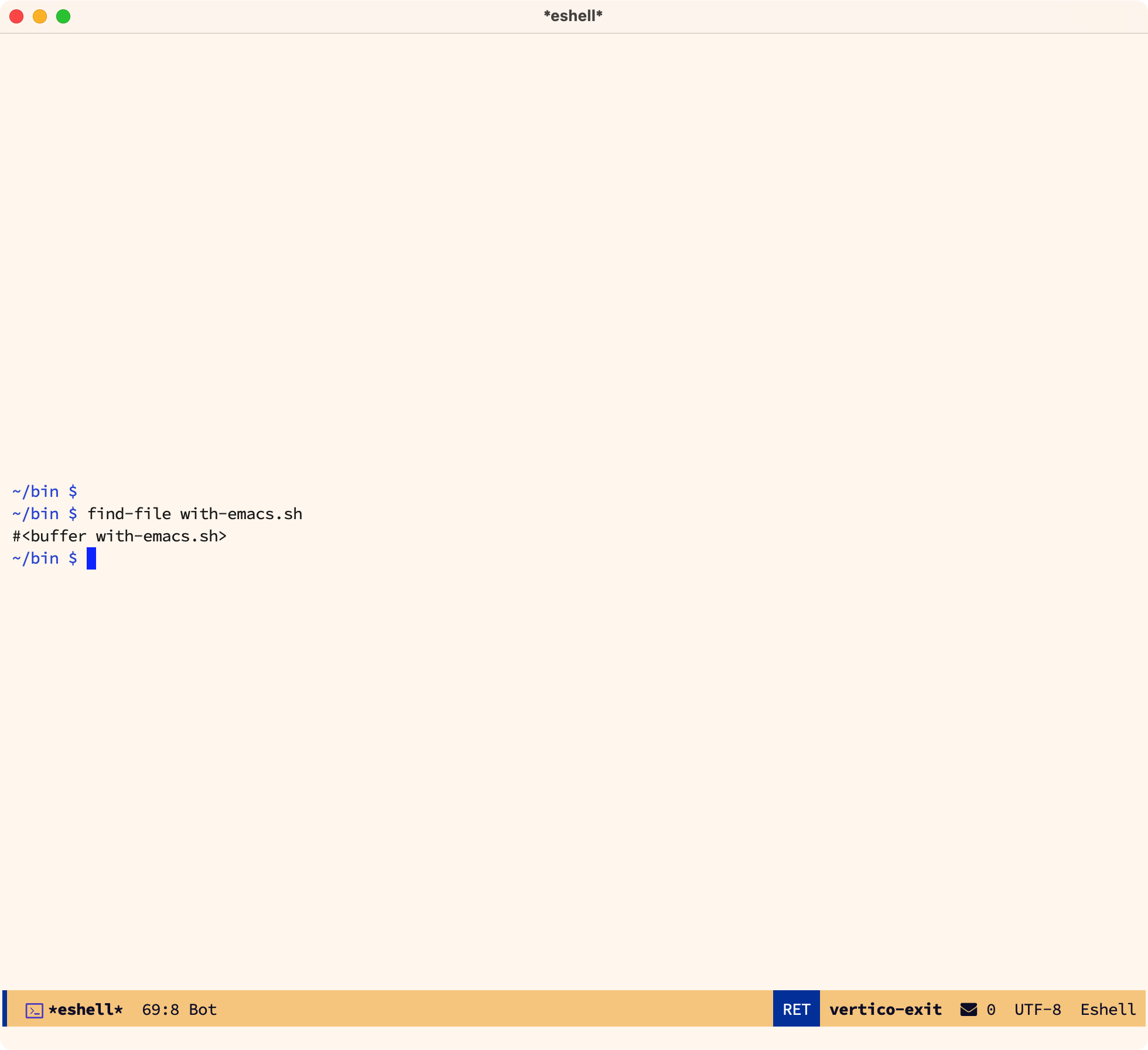
我们也可以在 eshell 里执行表达式:

由于水平和篇幅有限,这里不举出所有例子,感兴趣的同学可以自行阅读这篇文章:Mastering Eshell
4.2 eshell 的基本配置 🔗
Eshell 是开箱即用的,我们可以通过定义 eshell/xxx 函数来自定义一些 Eshell 里的命令,完全通过 Elisp 来实现,非常方便。
(use-package eshell
:ensure nil
:functions eshell/alias
:hook ((eshell-mode . (lambda ()
(term-mode-common-init)
;; Remove cmd args word by word
(modify-syntax-entry ?- "w")
(visual-line-mode 1)
(setenv "PAGER" "cat")))
)
:config
(defun term-mode-common-init ()
"The common initialization for term."
(setq-local scroll-margin 0)
(setq-local truncate-lines t)
)
;; 在Emacs里输入vi,直接在buffer里打开文件
(defalias 'eshell/vi 'find-file)
(defalias 'eshell/vim 'find-file)
;; 语法高亮显示
(defun eshell/bat (file)
"cat FILE with syntax highlight."
(with-temp-buffer
(insert-file-contents file)
(let ((buffer-file-name file))
(delay-mode-hooks
(set-auto-mode)
(font-lock-ensure)))
(buffer-string)))
(defalias 'eshell/cat 'eshell/bat)
;; 交互式进入目录
(defun eshell/z ()
"cd to directory with completion."
(let ((dir (completing-read "Directory: " (ring-elements eshell-last-dir-ring) nil t)))
(eshell/cd dir)))
;; 查找文件
(defun eshell/f (filename &optional dir)
"Search for files matching FILENAME in either DIR or the
current directory."
(let ((cmd (concat
;; using find
(executable-find "find")
" " (or dir ".")
" -not -path '*/.git*'" ; ignore .git directory
" -and -not -path 'build'" ; ignore cmake build directory
" -and -not -path '*/eln-cache*'" ; ignore eln cache
" -and -type f -and -iname "
"'*" filename "*'")))
(eshell-command-result cmd)))
:custom
(eshell-banner-message
'(format "%s %s\n"
(propertize (format " %s " (string-trim (buffer-name)))
'face 'mode-line-highlight)
(propertize (current-time-string)
'face 'font-lock-keyword-face)))
(eshell-scroll-to-bottom-on-input 'all)
(eshell-scroll-to-bottom-on-output 'all)
(eshell-kill-on-exit t)
(eshell-kill-processes-on-exit t)
;; Don't record command in history if starts with whitespace
(eshell-input-filter 'eshell-input-filter-initial-space)
(eshell-error-if-no-glob t)
(eshell-glob-case-insensitive t)
;; set scripts
(eshell-rc-script (locate-user-emacs-file "etc/eshell/profile"))
(eshell-login-script (locate-user-emacs-file "etc/eshell/login"))
)
4.3 eshell 的 alias 🔗
Eshell 里的 aliases,可以通过 tangle 的方式定义在 ~/.emacs.d/etc/eshell/aliases 这个文本文件里:
#+BEGIN_SRC text :tangle etc/eshell/aliases
alias ff find-file $1
alias fo find-file-other-window $1
alias d dired $1
alias ll ls -alh
alias l. ls -dh .*
alias up eshell-up $1
alias pk eshell-up-peek $1
alias less view-file $1
alias more view-file $1
#+END_SRC
4.4 eshell 里的 C-d 🔗
我们在使用 iterm 时,经常会使用 C-d 来结束窗口,而在 Emacs 里,这个快捷键绑定的是 delete-char 函数,我们通过下面的设置来让 C-d 更智能:
(use-package em-rebind
:ensure nil
:commands eshell-delchar-or-maybe-eof)
(use-package esh-mode
:ensure nil
:bind (:map eshell-mode-map
("C-d" . eshell-delchar-or-maybe-eof)
("C-r" . consult-history)
("C-l" . eshell/clear))
)
当光标后面有字符的时候,删除光标后的字符,当没有字符的时候,直接退出当前 shell。
4.5 eshell 的命令历史 🔗
我们通过下面的设置,扩大 eshell 的历史记录:
(use-package em-hist
:ensure nil
:defer t
:custom
(eshell-history-size 1024)
(eshell-hist-ignoredups t)
(eshell-save-history-on-exit t))
我们按下 C-r 后,可以通过 consult-history 来搜索命令历史,利用 Emacs 的补全机制,快速输入命令:
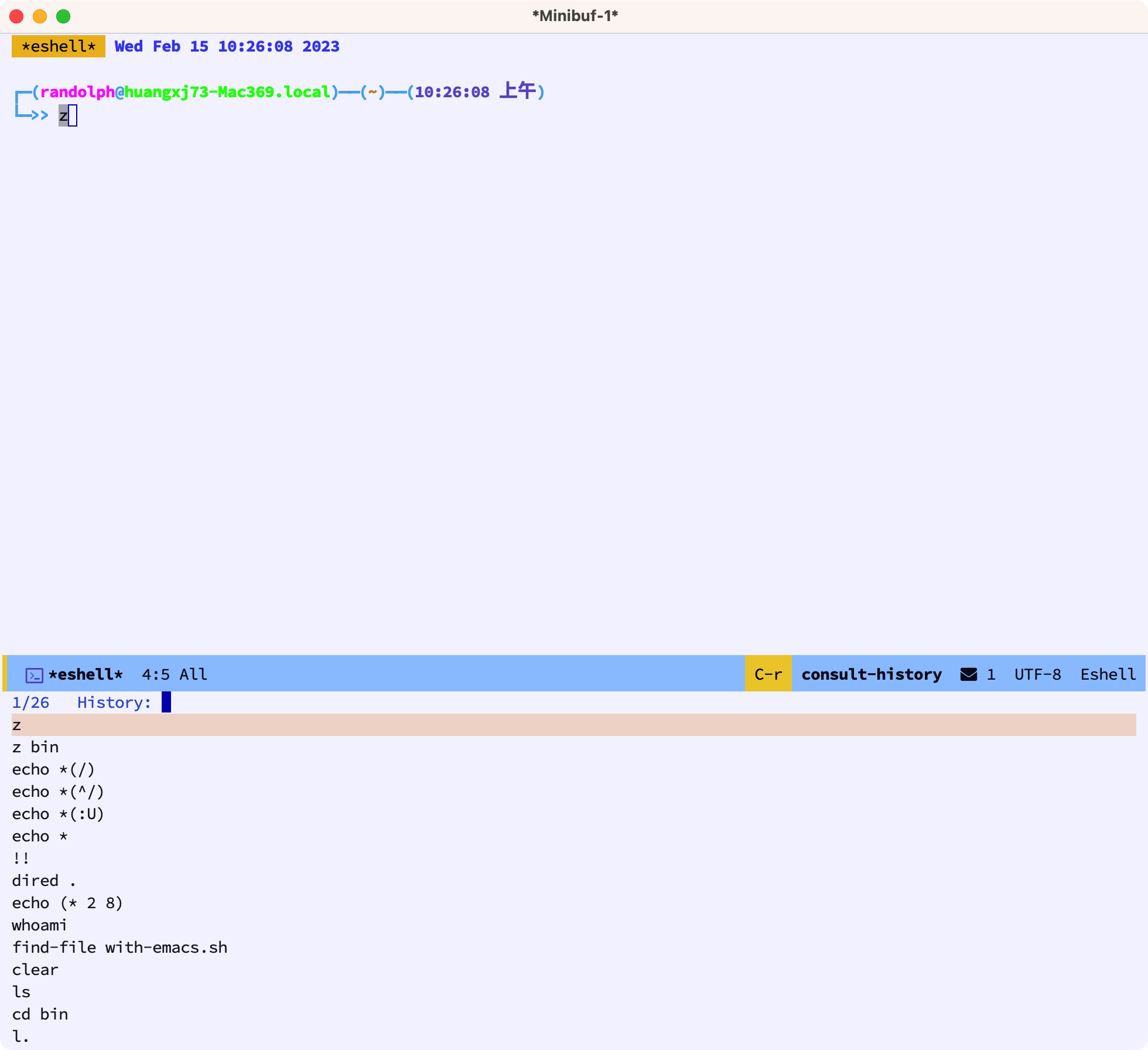
4.6 有些命令使用 term 🔗
有一些命令如 top,我们还是使用 term:
;; following commands will run on term instead
(use-package em-term
:ensure nil
:defer t
:custom
(eshell-visual-commands '("top" "htop" "less" "more"))
(eshell-visual-subcommands '(("git" "help" "lg" "log" "diff" "show")))
(eshell-visual-options '(("git" "--help" "--paginate")))
(eshell-destroy-buffer-when-process-dies t))
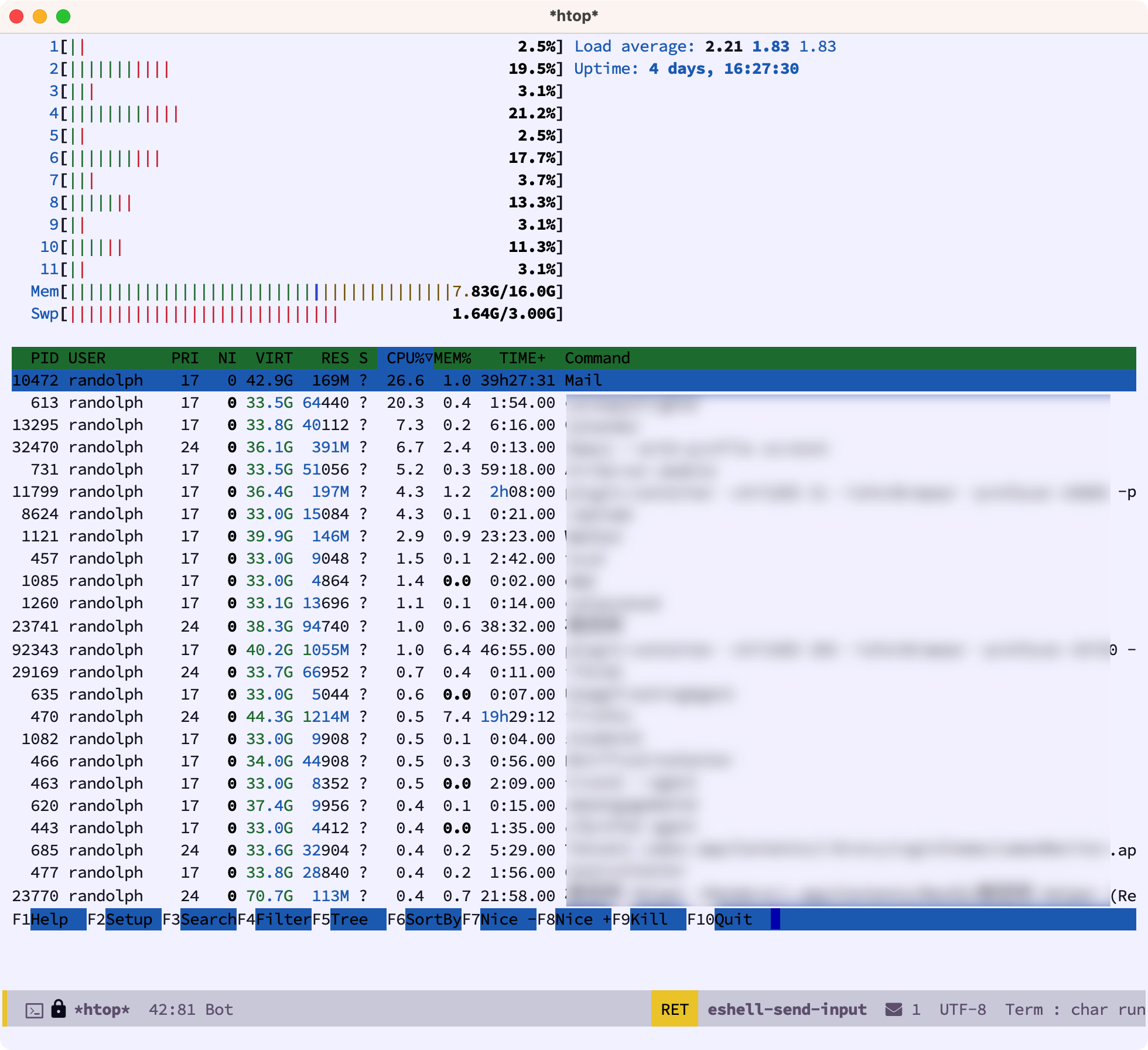
下面是在 Eshell 里运行 htop 的截图:
4.7 修改下 eshell 的主题 🔗
eshell-git-prompt 插件提供了数个好看的 Eshell 命令行主题。
(use-package eshell-git-prompt
:ensure t
:after esh-mode
:custom-face
(eshell-git-prompt-multiline2-dir-face ((t (:foreground "#c09035" :bold t))))
:config
(eshell-git-prompt-use-theme 'multiline2)
)
安装完插件后,我们可以看到 eshell 主题变得更好看了:

4.8 eshell-syntax-highlighting 语法高亮 🔗
eshell-syntax-highlighting 插件为Eshell提供语法高亮。
(use-package eshell-syntax-highlighting
:after esh-mode
:ensure t
:hook (eshell-mode . eshell-syntax-highlighting-global-mode)
:custom-face
(eshell-syntax-highlighting-shell-command-face ((t (:foreground "#7cc77f" :bold t))))
)
安装完这个插件后,我们输入正确的命令时,会以绿色显示,其他错误命令时,是棕色,很方便:
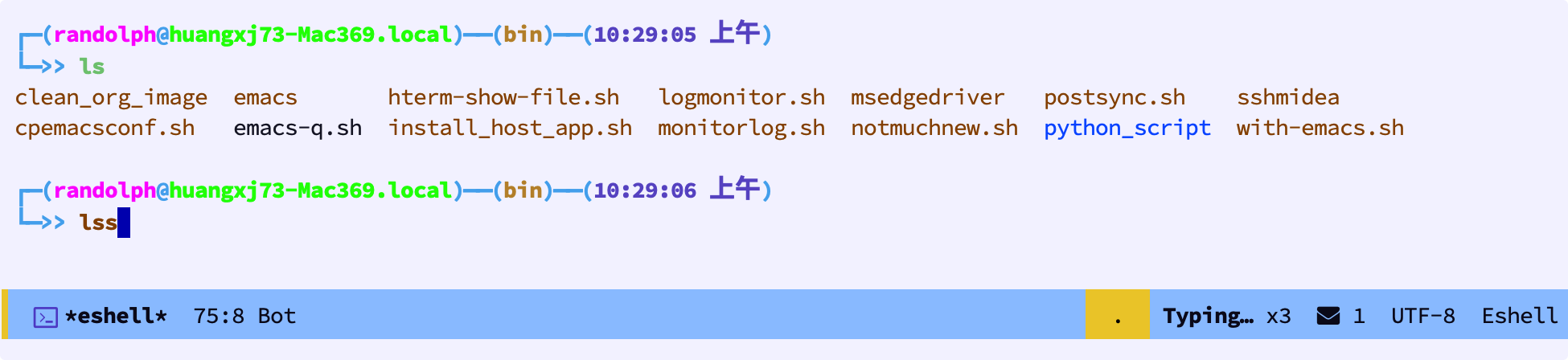
4.9 capf-autosuggest自动补全 🔗
capf-autosuggest 提供Fish类似的Eshell命令自动补全功能。类似的插件还有 esh-autosuggest。
(use-package capf-autosuggest
:ensure t
:hook ((eshell-mode comint-mod) . capf-autosuggest-mode)
)
安装完这个插件后,我们在输入某些命令时,会自动地根据你的命令历史,来提供候选补全,你可以按下 C-e 来补全,非常方便:

4.10 eshell-up快速进入父级文件夹 🔗
eshell-up 插件可以快速进入当前文件夹的任何一个父级文件夹。通过 up 命令(已经设置了alias)进入当前文件夹的任何一级父目录。
(use-package eshell-up
:ensure t
:commands (eshell-up eshell-up-peek)
:config
;; to print the matching parent directory before changing to it
(setq eshell-up-print-parent-dir t)
)
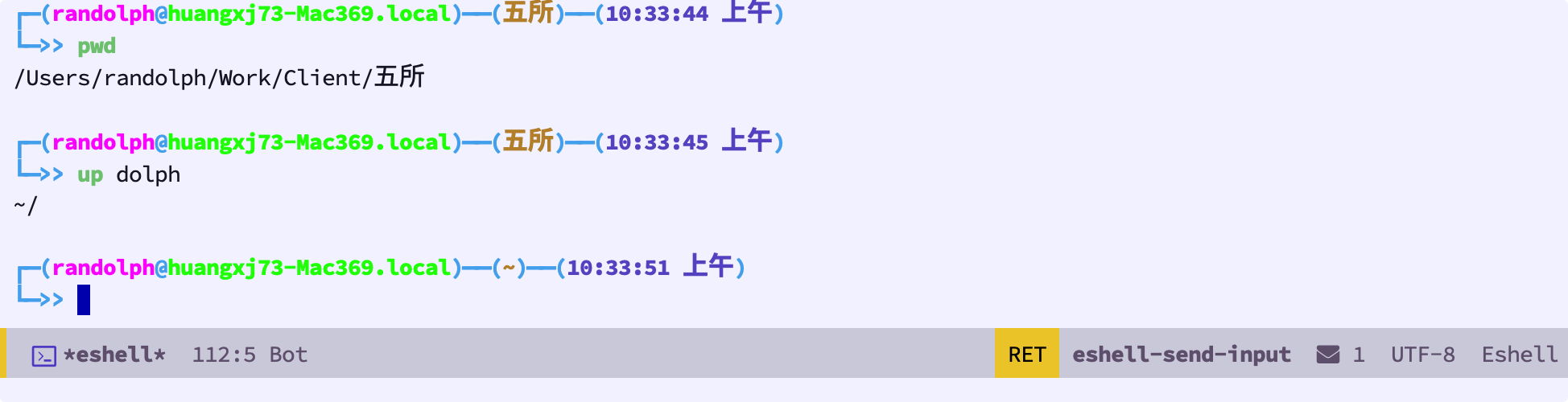
安装完这个插件后,我们可以快速的进入路径里的任何一个文件夹,非常方便:

你甚至都不用输全:
5 结语 🔗
通过今天的学习,我们了解了如何在 Emacs 里使用 Shell,尤其是 eshell,我们通过 eshell,可以很便利的在 Emacs 里执行一些命令操作,进一步的提升我们的工作效率!
这节课的配置文件的快照见:emacs-config-l23.org
你也可以在 这里 查看最新的配置文件。